Course 3 - Chemical Bonding
Time yourself: 15minutes
What is Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms or ions combine to form molecules or compounds.
😊Allow me to explain😊
Remember when we studied the atoms, we discovered that an atom cannot survive or be alone. In order to survive they must combine or join with the same element to form molecules(O2) or with different elements to form compounds (NaCl).
The process by which that happens is CHEMICAL BONDING.
So,
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms or ions combine to form molecules or compounds.
There are three main types of chemical bonding:
1. Ionic or electrovalent bonding.
2. Covalent bonding
3. Metallic bonding
Time yourself: 20minutes
Ionic or Electrovalent bond
This type of bond occurs when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, typically between metals and non-metals.
Remember OIL RIG
Oxidation is loss (of electrons)
Reduction is gain (of electrons)
In electrovalent/ionic bonding one will oxidize while one will reduce.
Then the opposite charges will create an electrostatic attraction that holds them together.
😊Let me use an example to explain better 😊
Our favorite natural cooking ingredient: NaCl (table salt).
NaCl is made of Sodium and Chlorine.
Remember I said ionic bonding occurs between metals and non-metals
Sodium is the metal and chlorine is the non-metal.
Na => 11
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s11
- Plans to lose that valence 1 to become stable.
Cl =>17
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
- Requires one electron to become stable.
So Sodium will transfer its 1 valence electron to Chlorine making sodium positive and chlorine negative.
Then an electrostatic force holds them together forming Na+Cl-.
Other examples:
1. MgO| Magnesium oxide:
Result: Mg2+O2-
2. CaF2| Calcium fluoride:
Result: Ca 2+F 2-
3. KBr| Potassium bromide:
Result: K+Br-
Remember Ionic or electrovalent bonding involves TRANSFER of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
Make sure you write whatever you remembered after read in your StudyHawkX lesson Note🙃.
Course 3 First Test
Read the questions carefully, then answer. Make me proud😁
Covalent Bonding
This kind of bond exists between non-metals.
It involves sharing of electrons, not oxidation and reduction.
For example, simple molecules like O2 Cl2 H2 are covalent bonds.
Also, in some compounds like water.
O2(8)
1s2 2s2 2p4 and 1s2 2s2 2p4
Oxygen atoms need two electrons to become stable, so it shares with another of its kind.
H2O
H2 => 1s1 and 1s1
O => 1s2 2s2 2p4
Here oxygen needs two electrons to be stable and hydrogen needs 1 atom to be stable, so two atoms combine with one oxygen atom in order share electrons with each other equally.
Diagrammatical explanation
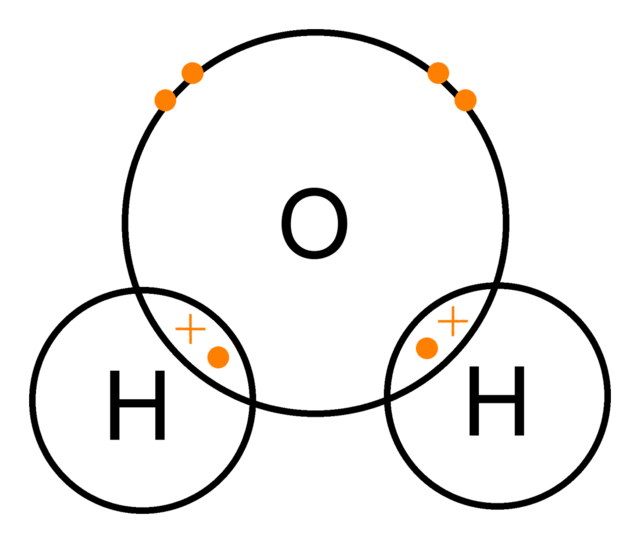
Remember, Covalent bonding involves SHARING of electrons transfer, and it occurs between non-metals.
Hope you learnt something, Pleas😿e I beg you😥 jot down what you read and don’t over study. Thank you!
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bond found in metals.
It occurs due to the attraction between a "sea" of delocalized electrons and the positively charged metal ions.
Metals are electropositive, meaning they have a tendency to lose electrons. These free electrons move around all the metal atoms in a pattern, creating a strong bond.
The delocalized electrons allow metals to be good conductors of heat and electricity, malleable (can be bent), and ductile (can be stretched into wires).
Metallic bonds are very strong because of the tight packing of atoms and the constant attraction between free electrons and positive ions.
Diagrammatic explanation
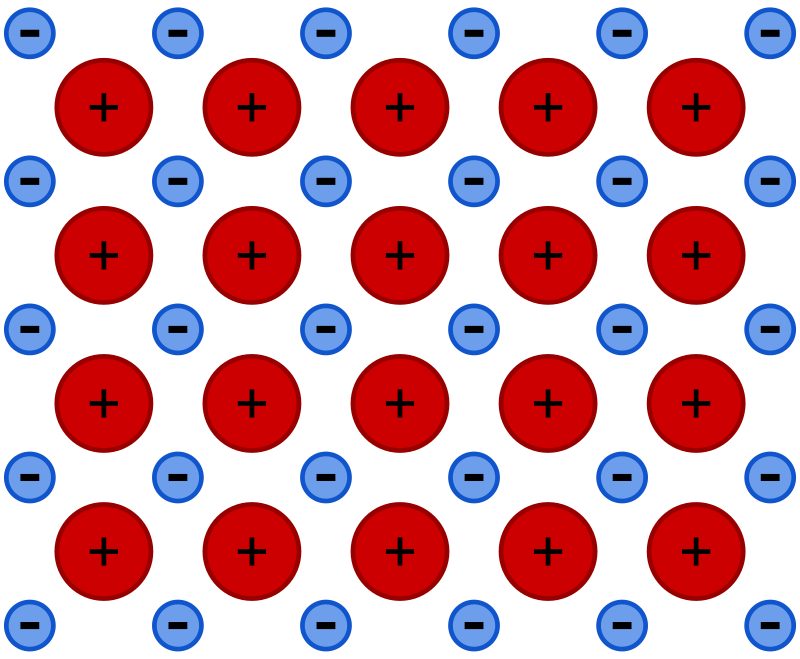
I hope it was understandable, Jot down what you learnt😁😁.
Intermolecular Forces
When you hear” intermolecular forces” we are talking about the forces the holds molecules together.
We have talked about bonding of atoms but now let’s see the forces that bonds two or more molecules together.
But we can’t start without a good definition:
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction between molecules.
Van der Waals forces
Van der Waals forces are the weakest attractions between molecules. They happen when electrons in molecules or atoms shift temporarily, creating a tiny charge that attracts another molecule. These forces are short-lived and very weak. Examples include the forces between molecules in helium, neon, or oxygen gas.
There are other intermolecular bonds like hydrogen bonding, but that’s a story for another day.
Revise for the Course 3 - Chemical Bonding final test💀.
Chemistry's Course 3 Final Test
Time yourself 10 minutes